The Truth About Neanderthals and Early Humans
Neanderthals Walked the Earth with Modern Man
Neanderthals, or Homo neanderthalensis, existed on Earth in the Late Pleistocene Age. They were a species of early human that some may not know actually walked the earth alongside modern humans.
DNA suggests that the species split from one another more than 300,000 years ago, and Neanderthals continued to live in Eurasia up until 40,000 years ago!
They Were Initially Thought to be Apes or Monsters
Due to the Neanderthal’s stockier build and shorter limbs, they were originally classified as ape-like creatures or monsters by early researchers in the 1900s. This was the time in which they were stereotyped as being slumping barbarians.

Source: ehowenespanol.com/ Pinterest
People began to associate barbaric qualities with “cavemen” and early humans, which led to their portrayal as monsters and antagonists in horror films.
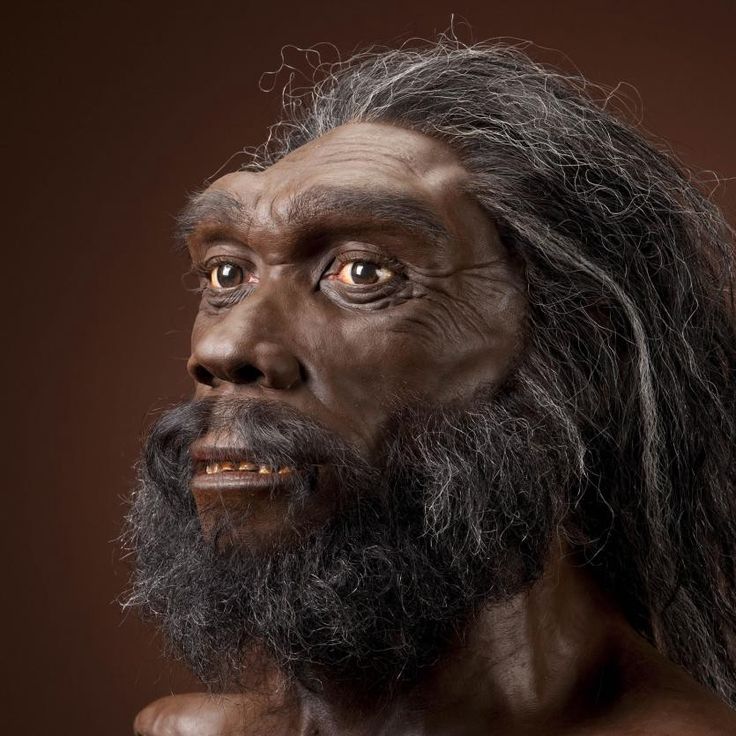
They Have a Closer Relative Than Homo Sapiens
Though Neanderthals are an ancestor to modern man, they actually have a closer relative in the Denisova people.

Source: medium.com/ Pinterest
The Denisovans are named after the cave in Siberia where their DNA was discovered in 2010. It was extracted from the finger bone of a teenage female who died 195,000 years ago!
They Were Mostly Europeans
Unlike their “cousins,” Homo sapiens and Homo erectus, who lived in Africa and Southeast Asia, Neanderthal remains have mainly been found in Western Europe.
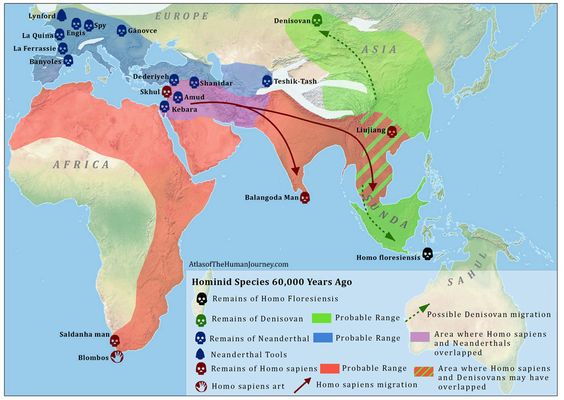
Source: atlasofhumanevolution.com/ Pinterest
Their name comes from the German Neander Valley, where their remains were found in 1856. Their migration patterns were directed by the weather and availability of food.
The Reason They Died Out
Neanderthals lived in a harsh world where 80% died before age 40, and their population numbers were low. Because of this, they suffered from the effects of inbreeding.

Source: Flickr.com/ Pinterest
Due to the lack of genetic diversity and the inheritance of detrimental traits, the Neanderthal species’ numbers dwindled, and they eventually disappeared altogether.
Their Build Was Pretty Different From Modern Humans
The reason Neanderthals were originally thought to be apes of some kind was that they were larger and more stout than your average man or woman.
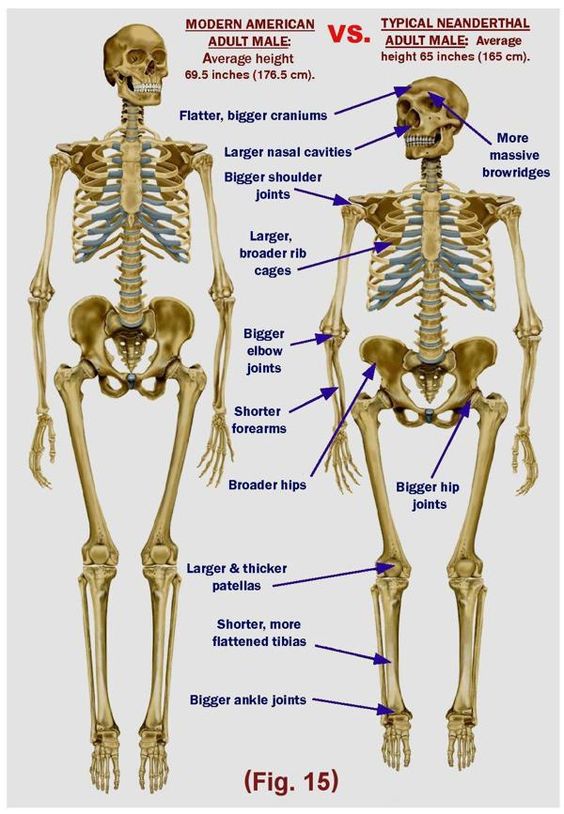
Source: Truthseeker NZ/ Pinterest
They tended to be on the short side, with males averaging about 5’4” and females clocking in at 5’, but also heavier on average than today.
Their Skulls Were Unique Too
If you’ve ever seen a side by side comparison of a contemporary human skull next to a Neanderthal, there are some pretty obvious differences.
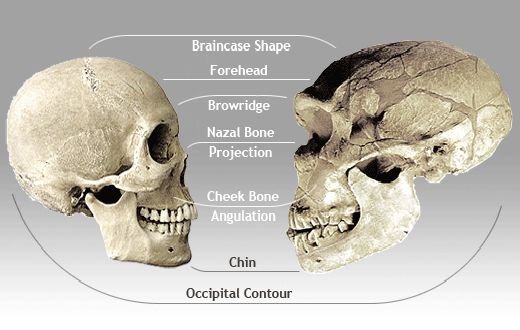
Source: bradshawfoundation.com/ Pinterest
Their cranial areas are somewhat sloped and much more oblong, and they have huge jaws to accommodate the larger teeth they had. They also have a noticeably larger nose.
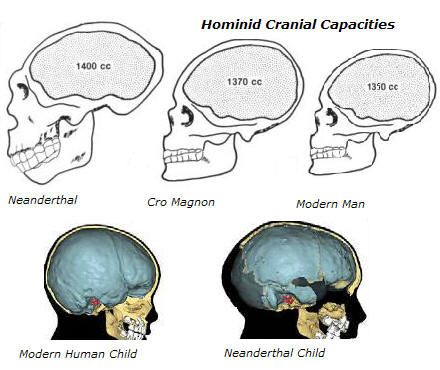
They Didn’t Have Tiny Brains
Quite the opposite, actually. Neanderthals, on average, had larger brains than their modern-day counterparts and were most likely capable of some spoken language.
Source: geocities.ws/ Pinterest
They also probably had better night vision than we do, based on the size of their eye sockets and the part of the brain that processes sight.
Some of Them Were Redheads
Neanderthals are often depicted as short, swarthy people, with dark hair and olive or deep tan skin, but many of them had a lighter complexion than you’d imagine.
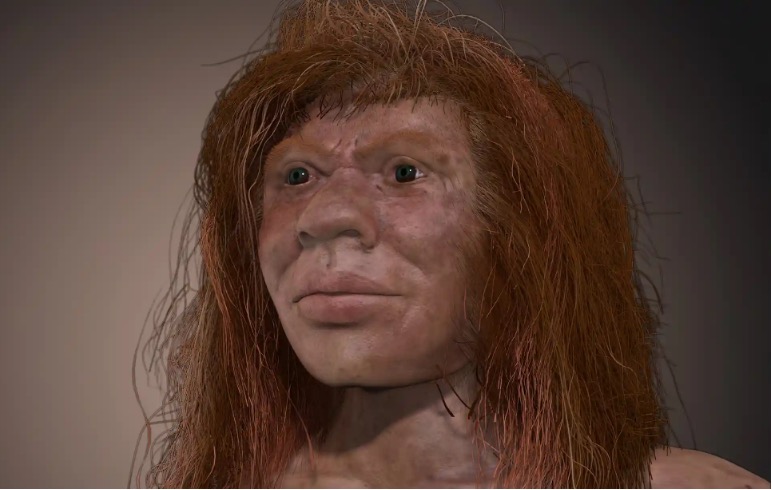

Photograph: John Bavaro/early-man.com
This was partially due to the colder, less sunny environment they lived in, but some also carried genes for lighter skin and hair.
They Had it Rough
Though technically Neanderthals would have been considered an alpha predator at the time they were alive, they still faced a lot of danger just to survive.
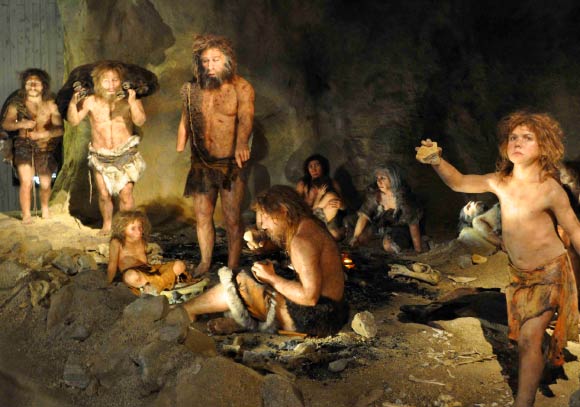

Image credit: Tyler B. Tretsven
Nearly all of the recovered specimens showed some signs of injury or trauma, and for many of them, it was their cause of death.
They Lived as Family Units
Much like other primates, Neanderthals lived in small, closely-knit family groups. Each of the family members would perform different roles like hunting and child-rearing.

Karen Carr
It appears from their skeletons that young children were most likely put to work early (yikes!) which stunted their growth and often led to injury.
They Organized Themselves Socially
A thriving population of Neanderthals would consist of up to 50 family units who would interact together, likely sharing duties such as hunting and trading. Men, women, and even kids were entrusted with hunting. This was perhaps less productive on the whole as it didn’t account for different talents or capabilities. However, it meant everyone shared the same basic survival skills.

Neanderthal Museum
Evidence shows that Neanderthals used their teeth as tools. Men had more wear on their upper teeth, while ladies had more wear on their lower teeth, suggesting there were some contrasts in their assignments. Since certain Neanderthals were found with special apparel and adornments, experts believe they might have had a hierarchy in their group between elevated elites and more common folk.
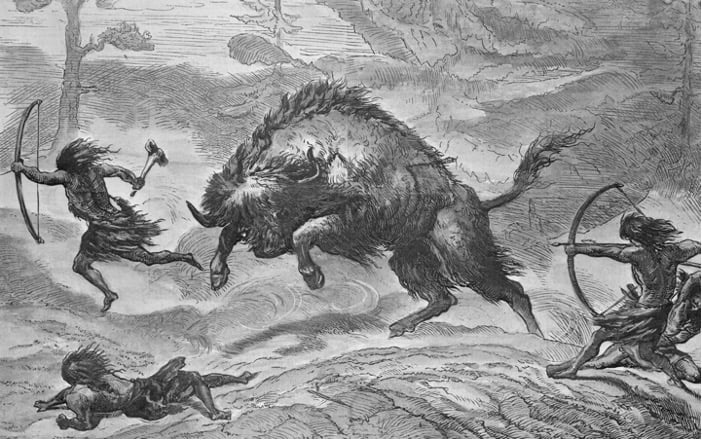
They Were Carnivores
Modern humans are omnivorous, and we often think of ancient peoples as being exactly the same; hunter-gatherers who ate what plants they could find while supplementing with animal protein.

State Archives of Florida
However, nearly all of their diet consisted of meat, which they hunted from animals like mammoths, boars, and ancient cattle called aurochs.
They Had Cooking Skills
Historical evidence shows that once Neanderthals obtained food, they knew how to cook it in a number of unexpectedly complex ways.

Pixabay
They knew how to make fires, and could roast, boil, and even smoke meats. They also occasionally used plants and herbs to add flavor and variety to their cooking.
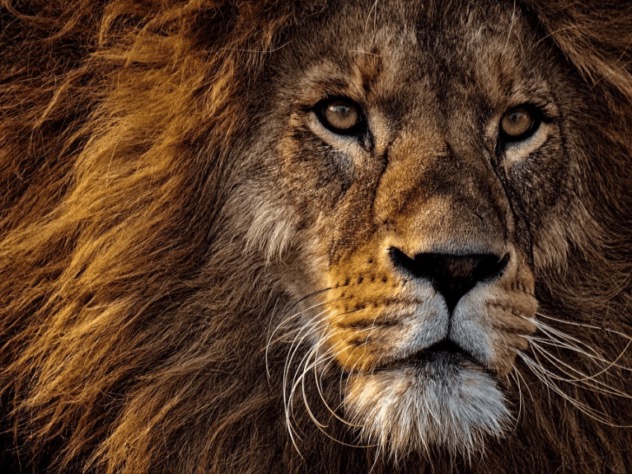
They Had Fierce Competition
Neanderthals weren’t the only predators roaming the ancient hills and valleys of Western Europe. They fought for territory with many different creatures.

Pixabay
Other carnivores like wolves, bears, and even cave lions. Despite the obvious threat of becoming food themselves, Neanderthals had to also compete with predators for animals to hunt.
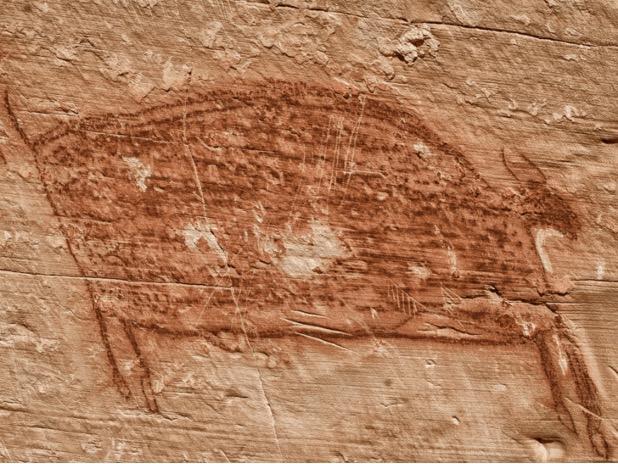
Art and Culture Were Important
One of the most important clues about the lives of early humans was the discovery of cave paintings, but they also made a wide variety of art using shells, feathers, and handmade beads.
Pixabay
The Neanderthals were an imaginative species, with incredible craftsmanship found in a few spots around the world. Scientists and researchers have found evidence of sculptures, carvings, and even jewelry that shows Neanderthals were more creative than you’d think.
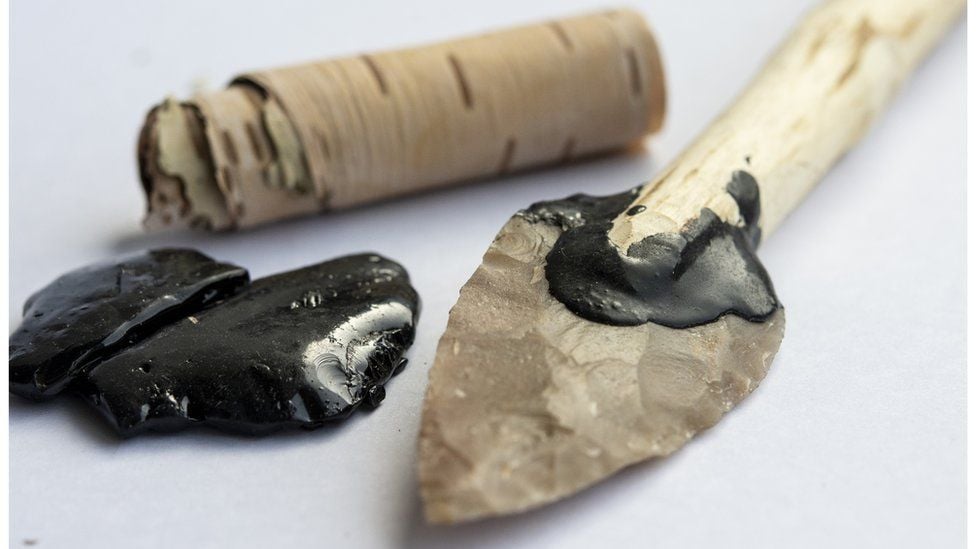
They Used Specialized Tools
We know from the artifacts they left behind that Neanderthals were actually capable of making quite sophisticated tools like knives made from bone and rock.

PAUL R.B. KOZOWYK
They could wield fire and build hearths. They were also talented weavers and used fibrous materials to construct nets, baskets, clothes, and even shoes.
Their Techniques Are Still Used Today
We think of early human technology being extremely primitive and outdated in our era of highly advanced electronics and the internet. However, some of their tools have stuck around.

ArchaeologySouthwest.org
To this day, leather workers use similar scraping and cutting tools to the ones Neanderthals used to prepare animal hides.
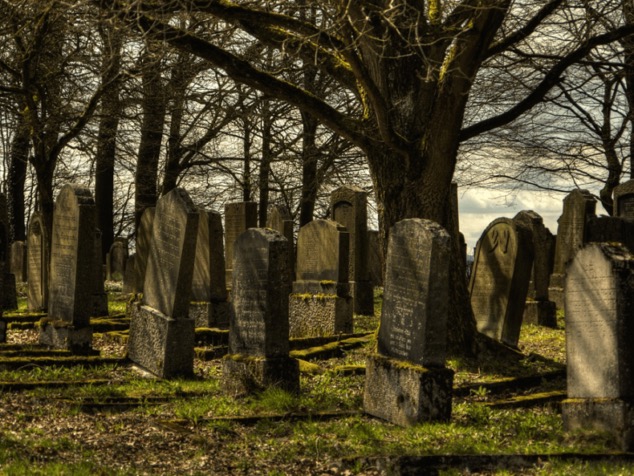
They Honored Their Dead
This is yet another way that Neanderthals and other early humans displayed an unexpected level of organization and emotional capacity.

Pixabay
Graves and burial sites containing ancient remains have been discovered, leading scientists to believe that their dead were honored and celebrated in a ritualistic manner rather than abandoned carelessly.
They Communicated with More Than Grunts
Despite their ape-like appearance and features, Neanderthals were actually thought to be capable of fairly complex speech patterns and even basic language.

Image credit: Abel Grau, CSIC Communication
Because their anatomy relating to speech is actually quite similar to modern humans, scientists think their methods of communication were closer to ours than to animals.
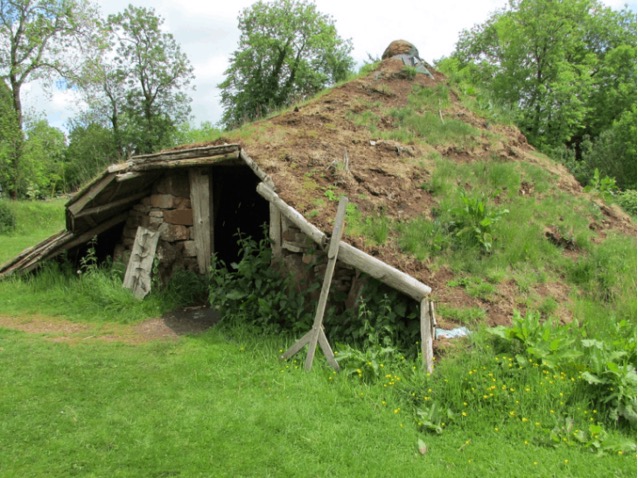
They Weren’t Just Nomads
Though the populations of Neanderthals did change over time as they migrated around the continent, they did occasionally settle down and build permanent homes.

Pixabay
These weren’t just simple caves, either. They were hand-built structures with distinct rooms, each intended for specific uses like cooking, sleeping, social space, and storage.
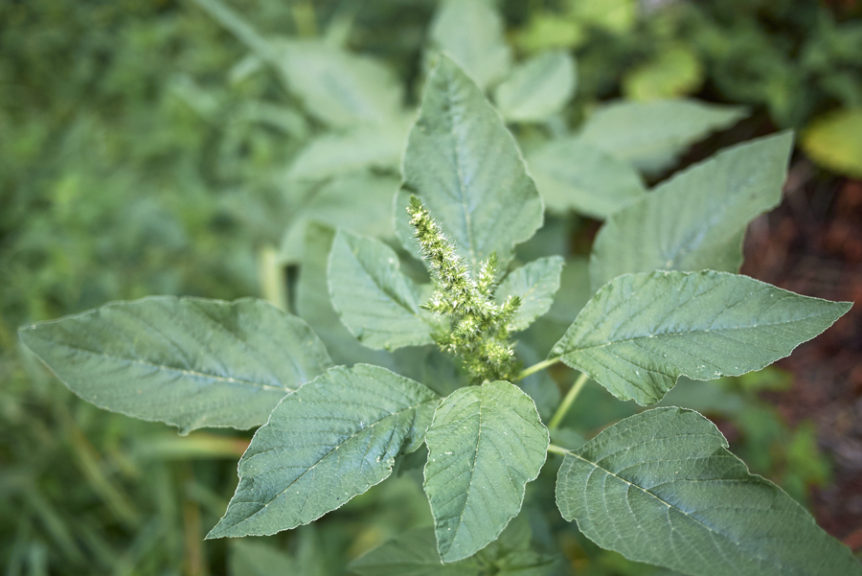
They Used Food as Medicine
The Neanderthal’s diet did consist of nearly 90% meat, but that’s not to say they never ate their veggies!

Amaranthus retroflexus plant
They may not have been big on salads, but they used plants in a medicinal manner, both by eating them and using them as topical agents to relieve pain and infection.
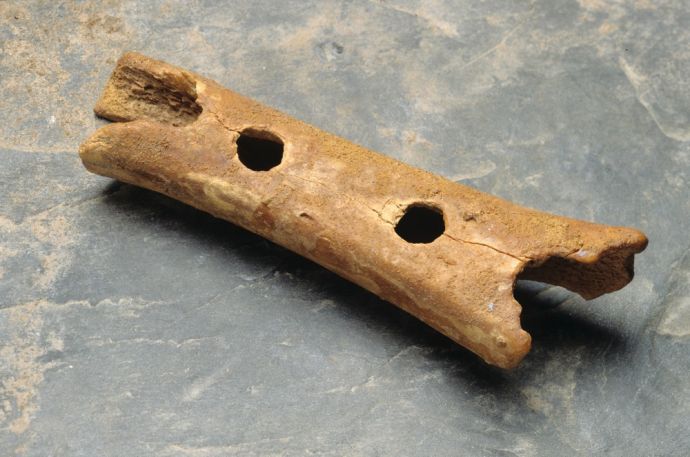
They Made Musical Instruments
At this point, we shouldn’t be surprised to know that early humans were actually a lot more like us than we thought. They may have even composed music on primitive instruments.

Tomaž Lauko
A simple flute-like device made from bone was discovered in Slovenia and was thought to have been created by Neanderthals.
They Raised Their Young with Care
Life was brutal for early humans, and many never survived past age 40 due to injury or illness. They still managed to raise children, however.
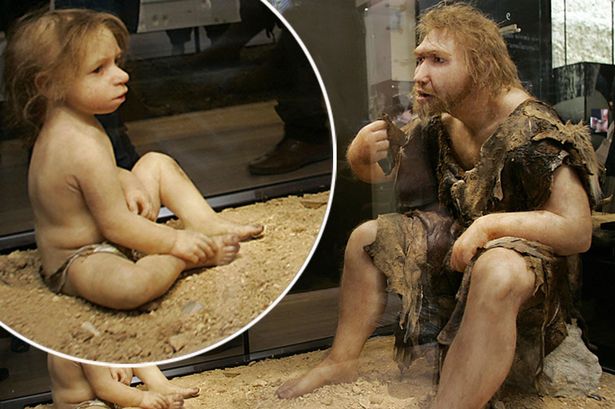

Image: Getty
They were shown through art and fossil evidence to be an important part of the family unit and were often given more elaborate burial rituals.
They Cared for Their Communities
While many individuals imagine that Neanderthals only thought about themselves and didn’t put in the effort to focus on others, there is evidence that this isn’t the situation. The Neanderthals were committed to tending for the sick and the elderly in their communities. In 1908, further evidence of this was found on a 56,000-year-old Neanderthal skeleton unearthed in France.

pikabu
When the man passed, he was old and had lost the majority of his teeth. His remains show that he probably had assistance crushing down his food so he could eat it. Moreover, his bones gave indications of joint pain and breaks, which means different individuals from his group would have needed to assist him with moving around.
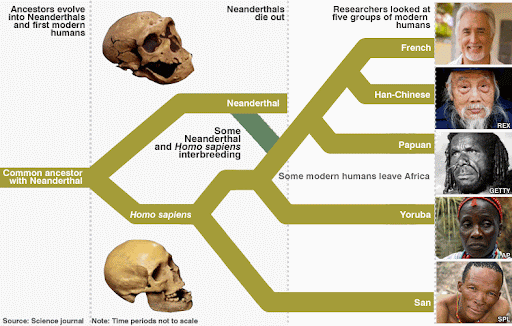
Humans Aren't Direct Descendants of Neanderthals
It is common for many to believe that humans directly evolved from Neanderthals. However, this is not the case. The Neanderthals and Homo sapiens stemmed from two distinct groups. After all, we just covered how these groups lived simultaneously on Earth for a few thousand years.
Source: Science Journal
Scientists have begun to understand that the origin of Neanderthals dates back to a specific evolutionary line. Thus, you can think of Neanderthals as distant cousins to the humans of modern day.
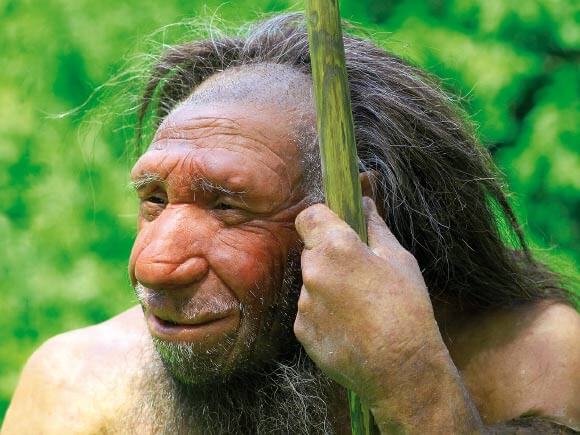
Neanderthals Had Tough Skulls
Proof of a Neanderthal who suffered an interesting injury was found in 1856. The Neanderthal bones presented an old elbow injury, and the interesting part is that the fracture had been mended. From that point forward, every Neanderthal skeleton that has been found has displayed some physical trauma.

Source: TheLovePost
Numerous Neanderthal skeletons have demonstrated indications of injuries around the head and neck. A few years ago, experts asserted that the recurrence of these wounds would make Neanderthals somewhat like present-day rodeo cowboys. As of late, proof of these kinds of wounds in Pleistocene people that lived during a similar time as the Neanderthals has been found. This suggests that the Neanderthals were tough enough to withstand numerous head and neck injuries without experiencing trauma.
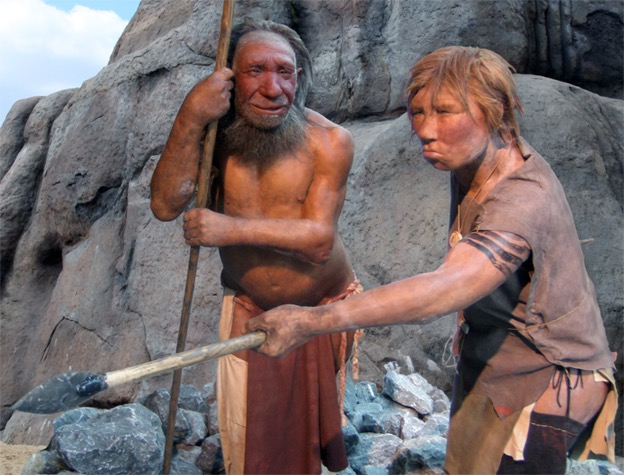
They Had Good Coordination
As discussed previously, the Neanderthals often got injured but were resilient and bounced back well. Proof of this can be found in practically every Neanderthal skeleton that has been unearthed to date. From skull fractures to broken bones, the Neanderthals were tough creatures.

Source: UNiesert / Frank Vincentz / Wikimedia Commons
Though they experienced plenty of injuries, that doesn’t mean the Neanderthals had poor coordination. They hunted enormous animals like reindeer and buffalo with simple spears. The Neanderthals utilized a technique for hunting that included sneaking up on prey and ambushing them. With that said, they displayed good coordination. The injuries resulted from the perils of life back then, not clumsiness.
Neanderthals and Humans Had Different Cognitive Abilities
Neanderthals were intelligent and were very creative for their time. They showed decent intellectual capacities, but that doesn’t mean they were as advanced as modern people. While a few overlaps in behaviors were observed, a modern human likely wouldn’t have much in common with the average Neanderthal.
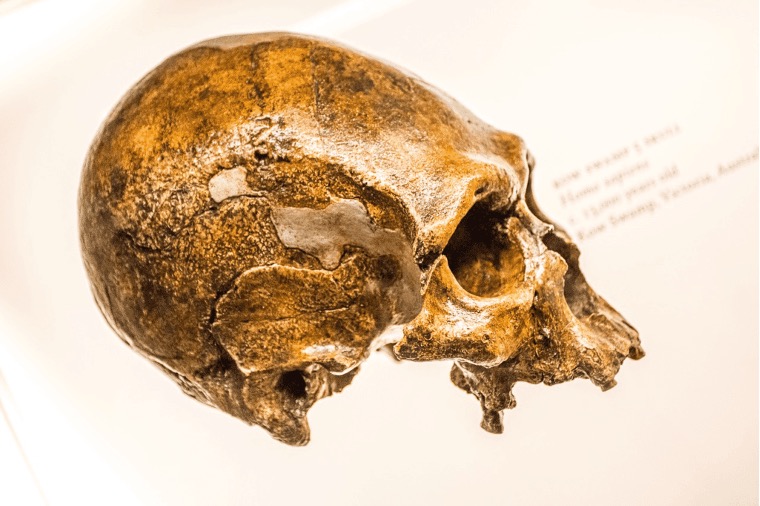

Source: Pixabay
The language would be unique, as would the capacity to understand and process information. Indeed, even in the Upper Paleolithic period, Europeans would have different intellectual capacities in comparison to the Neanderthals. Though we share a lot of similarities, in some ways, we have always been worlds apart.
They Hunted in Groups
Arguably, the Neanderthals discovered strength in numbers. They chased major game utilizing hand-made spears. While many people assume that the Neanderthals must have worked alone, that was not the situation.
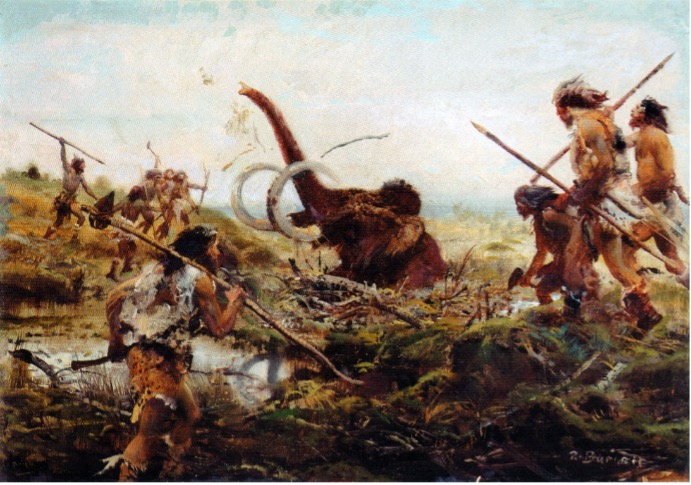

Source: UCL
The Neanderthals hunted huge creatures like deer, elephants, and mammoths, and they also had to defend themselves against the apex predators of the time. It wasn’t unusual for Neanderthals to be killed by their animal rivals. For these reasons, the Neanderthals worked in groups to keep themselves more secure. In doing so, they could remain safe and successfully chase their prey.
Neanderthals Were Actually a Successful Species
If the Neanderthals were so profoundly gifted, why did they succumb to extinction? They were able to communicate, perform rituals, and set up their own way of life. What held them back from boldly evolving into the future as humans did?

Source: Pixabay
Archeologists see the Neanderthals as a prosperous species due to how they lived. They were able to thrive in conditions that were often harsh and unforgiving. The Neanderthals withstood more brutal environments than any other primates, and most modern people wouldn’t be able to live their life for even a week. They had opposable thumbs and certainly did not go extinct due to a lack of skills.
Neanderthals and Humans Are Quite Different
In light of the misconceptions about Neanderthals, it’s easy for individuals to expect that Homo sapiens are the “better” species. This assumption arises from the fact that Neanderthals went extinct while Homo sapiens didn’t, suggesting that we were able to thrive while they failed.

Source: Pixabay
We’ll never know exactly how a Neanderthal and a modern human would stack up in competition, and that’s alright. We can simply drop the old stereotypes and think of Neanderthals as our far-off cousins who displayed intelligence, creativity, and strength under testing conditions, helping to lay the foundation for our modern way of life.